Bram Koese / Wikipedia

Bram Koese / Wikipedia
N/A
N/A
Introduced pathogen; Brought to the UK and Ireland by non-indigenious crayfish species, particularly signal crayfish.
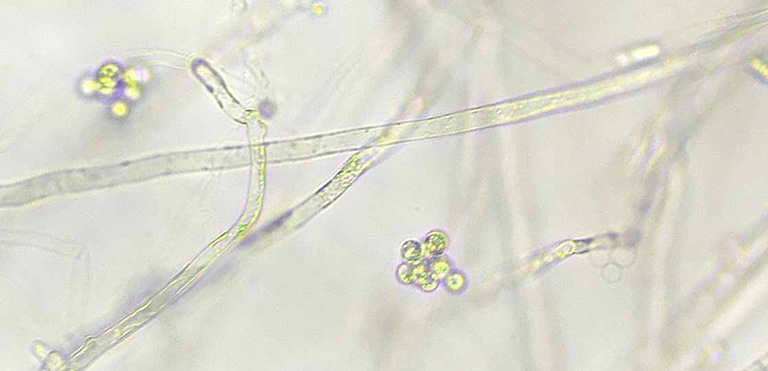
Disease carried by North-American crayfish but particularly, signal crayfish. This water mould can wipe out entire populations of white-clawed crayfish within weeks of initial infection. Spreads through water-borne spores which are released from infected crayfish.
Crayfish plague has been reported in Ireland since 2015 and is thought to be attributed to spore release from infected non-indigenous crayfish, contaminated gear, and equipment moving between waterbodies and the release of ornamental crayfish into the wild. Recently, a newly-discovered, close-related species, Aphanomyces fennicus spp., was found to be being amplified on the most-used qPCR assay and giving false-positive results for crayfish plague. At SureScreen Scientifics, we now use the most recent assay alongside internal negative and positive controls to ensure we provide customers with accurate results.
Detectable all year round due to the presence of spores. However, it is recommended to avoid the winter months when extreme weather conditions can cause a dilution of detectable DNA.